Ground Radiation Technology is based on the characteristic modes that are excited in the arbitrary ground plane, producing a very small-sized antenna with good radiation performances. Unlike the conventional quarter wavelength internal antennas, the Ground Radiation Technology requires a very small ground slot with lumped elements, which generates a large loop-type currents formed in the ground plane. The characteristic mode on the ground plane can then be strongly coupled if the loop-type currents are close to the magnetic field maximum of the ground plane. This new technology was widely used for the IoT Modules, TWS Bluetooth headsets, WiFi Modules, GNSS navigation positioning systems, and 5G smart phones, able to provide sufficient bandwidth efficiency and determine the radiation directivity according to the customer requirements. The R&D results show that the signal quality can be significantly improved compared to the traditional antenna design methods, especially at MIMO system applications.
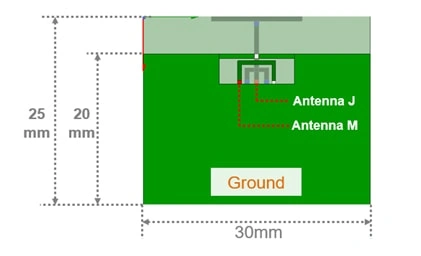
2 x 2 MIMO antennas are placed in a 30mm x 25mm ground plane, which is the size used in WiFi modules.
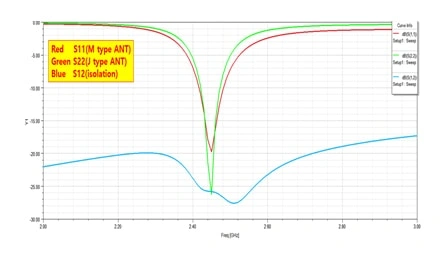
Two different antenna types independently excite the different ground modes, obtaining good isolation.
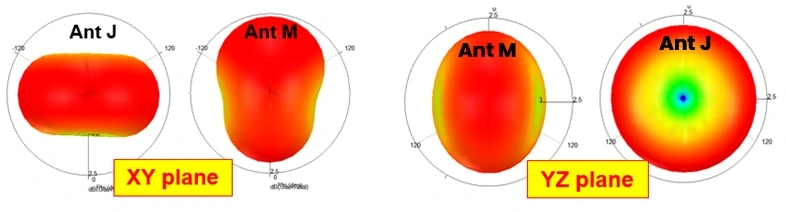
The computed results show that the antenna J source and the antenna M source produce the orthogonal radiation patterns at xy-plane and yz-plane, illustrating the good isolation of the two antennas.
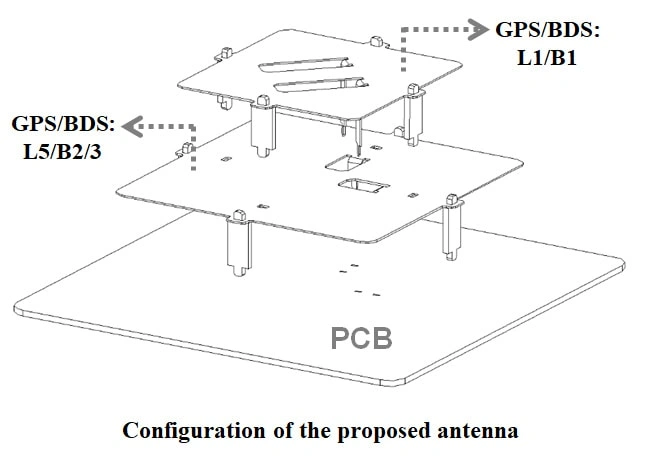
The capacitive elements are installed at the electric field maximum of the patch antenna, inducing the orthogonal current modes, as shown in Figure1.
1:Light-weight: compared to the conventional ceramic patch antenna, the weight of the air-medium patch antenna is reduced more than 60% which is useful for UAVs.
2:Controllable radiation pattern: the radiation patterns can be adjusted by the capacitive elements without varying the antenna gain and axial ratio.
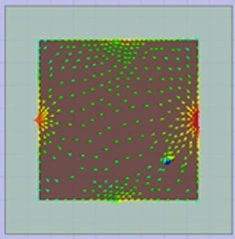
(a) B1transverse current
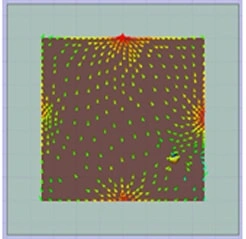
(b) B1Vertical current
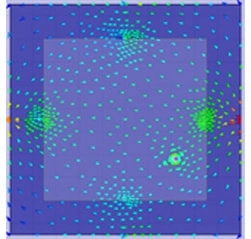
(c) B3transverse current
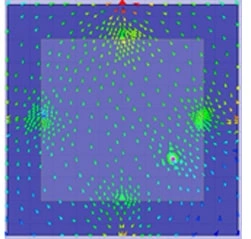
(d) B3Vertical current
As shown in Figure1, two antennas are placed very close to each other, where the distance between the antennas is only 1mm. The one is formed by a loop with capacitor called M-type antenna, and the another one is a monopole antenna designed like “T”, called J-type antenna.
The ground plane exists J1 and J2 ground modes alone x-axis and y-axis, respectively. The two ground modes are orthogonal. The M-type antenna only excites J1 and the J-type antenna only excites J2, obtaining good isolation and the orthogonal radiation patterns between two antennas, as shown in Fig.2 and Fig. 3.

2 x 2 MIMO antennas are placed in a 30mm x 25mm ground plane, which is the size used in WiFi modules.

Two different antenna types independently excite the different ground modes, obtaining good isolation.

The computed results show that the antenna J source and the antenna M source produce the orthogonal radiation patterns at xy-plane and yz-plane, illustrating the good isolation of the two antennas.