MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) antenna development involves designing and implementing antenna systems capable of supporting multiple simultaneous data streams to improve communication performance in wireless systems. Here's an overview of the steps involved in MIMO antennadevelopment:
Requirements Analysis: Understand the specific requirements of the wireless communication system for which the MIMO antenna system is being developed. This includes considerations such as data rate, coverage area, frequency bands, and environmental conditions.
Antenna Design: Design the individual antennas that will be used in the MIMO system. This may involve selecting antenna types (such as patch antennas, dipole antennas, or helical antennas), determining the number of antennas needed, and optimizing antenna parameters like impedance matching, radiation pattern, and polarization.
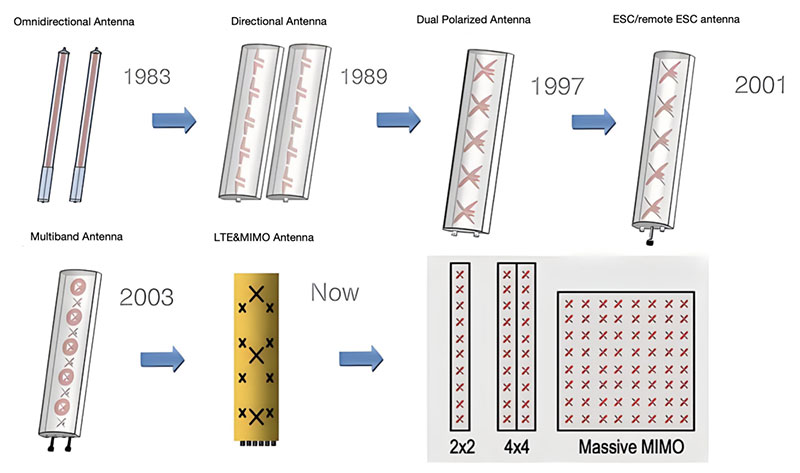
Array Configuration: Determine the configuration of the antenna array for the MIMO system. This includes deciding on the spatial arrangement of the antennas (e.g., linear, planar, or 3D array), antenna spacing, and antenna orientation. The array configuration plays a crucial role in achieving spatial multiplexing gains and improving diversity performance.
Channel Modeling: Develop accurate channel models to simulate the wireless propagation environment in which the MIMO antenna system will operate. This involves characterizing factors such as multipath fading, shadowing, and interference, which impact the performance of the MIMO system.
Beamforming and Spatial Processing: Implement beamforming techniques to optimize signal transmission and reception in the MIMO system. This may involve digital beamforming algorithms or analog beamforming using phase shifters. Spatial processing techniques such as precoding and spatial multiplexing are also used to maximize the throughput and reliability of the MIMO system.
Prototype Development: Build prototypes of the MIMO antenna system based on the design specifications. This may involve fabricating the antennas, constructing the antenna array, and integrating the necessary RF front-end components.
Testing and Validation: Conduct extensive testing and validation of the MIMO antenna system in laboratory and real-world environments. This includes measuring key performance metrics such as throughput, bit error rate (BER), signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and coverage range to ensure that the system meets the design requirements.
Optimization and Iteration: Fine-tune and optimize the MIMO antenna system based on the testing results and feedback. Iterative refinement may be necessary to address any performance limitations or issues identified during testing.
Deployment and Integration: Deploy the MIMO antenna system in the target wireless communication network and integrate it with the existing infrastructure. This may involve collaboration with network operators, equipment vendors, and other stakeholders to ensure seamless integration and interoperability.
Continuous Improvement: Monitor the performance of the deployed MIMO antenna system and incorporate feedback for continuous improvement. As wireless communication standards evolve and new technologies emerge, ongoing research and development efforts are needed to enhance the capabilities and efficiency of MIMO antenna systems.

