MIMO stands for Multiple Input Multiple Output. In the context of antennas, MIMO refers to a technology used in wireless communication systems where multiple antennas are used at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance.
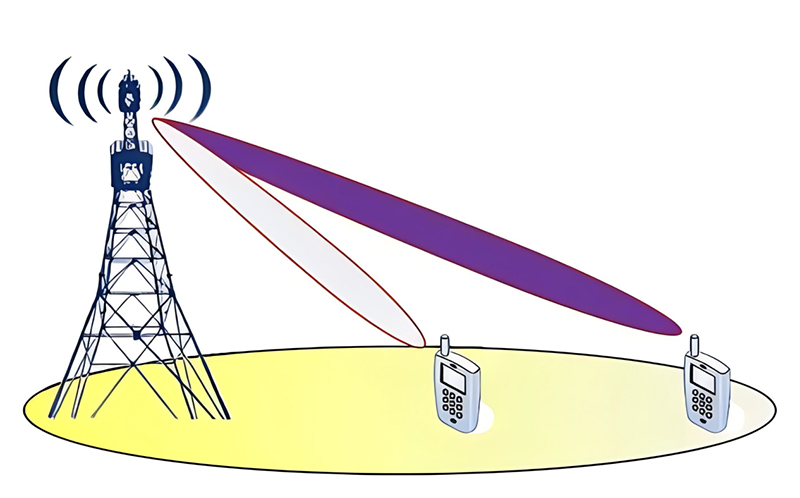
Traditional wireless systems typically use a single antenna at both the transmitter and receiver. However, MIMO systems use multiple antennas at both ends, allowing for the exploitation of multipath propagation to enhance data throughput, improve reliability, and increase spectral efficiency.
There are several configurations of MIMO antennas, including:
SIMO (Single Input Multiple Output): One transmitter antenna and multiple receiver antennas. This configuration is often used in diversity reception to improve signal reliability in environments with fading.
MISO (Multiple Input Single Output): Multiple transmitter antennas and one receiver antenna. This configuration can provide spatial multiplexing gains, allowing for higher data rates.
SIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output): Multiple transmitter antennas and multiple receiver antennas. This is the most common MIMO configuration and offers both diversity and spatial multiplexing gains.
MIMO antennas can be implemented in various forms, such as:
Multiple antennas on the same device: For example, multiple antennas on a smartphone or a Wi-Fi router.
Multiple antennas in an array: This can be a linear array, planar array, or any other geometric arrangement. Arrays allow for precise control of radiation patterns and can be used for beamforming.
Smart antennas: These antennas use techniques like beamforming and spatial multiplexing to improve performance by dynamically adjusting the radiation pattern based on the channel conditions.
MIMO technology has become a cornerstone in modern wireless communication standards like 4G LTE, 5G, and Wi-Fi, enabling higher data rates, better coverage, and improved reliability in wireless communication systems.

